™
H - 14 STRAY CURRENT CORROSION
A. General
C. Corrosion Prevention
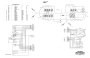
Anticorrosion anodes are attached to the bottom of the
gimbal housing of your stern drive or to the transom
Electrically induced underwater corrosion occasionally and propeller shafts (inboards models) to prevent cor-
affects boats and their related components. This is rosion to your electrical systems and underwater parts.
referred to as “Stray Current Corrosion” and appears These anodes will be slowly eroded away by galvanic
as surface pitting or deterioration. Stray current corro- action and require periodic inspection. Please refer to
sion is the decomposition of chemical compounds by the section on “Anti-Corrosion Anodes” in your engine
electric current.
manufacturer’s manual for additional information. See
Figure H4.
Stray current corrosion can be caused by surrounding
boats; an improperly wired battery/charger installation
or other boats that are in close proximity which have
electrical power leakages. Stern drive units are espe-
cially vulnerable to stray current corrosion.
Periodically inspect the engine components to de-
termine if corrosion damage exists. If stray current
corrosion damage is found, determine and correct the
cause of the stray current to prevent further damage.
Consult an experienced marine electrician or contact
your Four Winns dealer for assistance.
The use of some shore power battery chargers, while
the boat is in the water and the battery is connected to
the system, can cause stray current corrosion. Have
an experienced marine electrician review any battery
charger installation to ensure a stray current corrosion
problem will not develop. An improper battery connec-
tion is a common cause of stray current corrosion.
Transom
Anode
Shaft
Anode
NOTICE
Use only a battery charger designed to meet
U.S. Coast Guard regulations for external igni-
tion protection.
Figure H4: Inboard Transom & Shaft Anodes Shown
Corrosion is usually more prevalent in polluted or salt
water than in clean water. It is also more likely to occur
when dockage is in an area with steel piers, large metal
boats, or where shore power is in use.
B. Galvanic Corrosion
Galvanic corrosion results from a potential electrical dif-
ference existing between dissimilar metals immersed in
a conductive solution (e.g., salt or brackish water). If
these metals touch or are otherwise electrically con-
nected, this potential difference produces an electron
flow between them. The attack on the more active
metal is usually increased and the attack on the less
active metal is decreased, as compared to when these
metals are not touching.
Vista™ Owner’s Manual
Section H
Page 13
| Categories | Four Winns Manuals, Four Winns Vista Manuals, Outboard Marine Corporation Manuals |
|---|---|
| Tags | Four Winns Vista 248, Four Winns Vista 268, Four Winns Vista 288, Four Winns Vista 298, Four Winns Vista 328, Four Winns Vista 348 |
| Model Year | 2004, 2005, 2006, 2007, 2008 |
| Download File |
|
| Document Type | Owner's Manual |
| Language | English |
| Product Brand | Boats and Cruisers, Four Winns. For support contact your dealer at http://www.fourwinns.com/locate-dealer.aspx |
| Document File Type | |
| Publisher | fourwinns.com |
| Wikipedia's Page | Outboard Marine Corporation |
| Copyright | Attribution Non-commercial |
(3 votes, average: 4.67 out of 5)
Marine readers have rated 2004-2008 Four Winns Vista 248 268 288 288 298 328 348 Boat Owners Manual 4.7 out of 5.0 based on 3 product reviews. i like this boat